Description#
- Build a model based on a fine-tuned one using PyTorch Lightning on Google Colab Pro.
- Optimise hyperparameters and visualise evaluation metrics with Weights & Biases.
Introduction#
- This article gives a brief introduction to implementing a minimal action recognition model using a pre-trained model (3D ResNet).
- It does not cover tuning methods such as data augmentation or learning rate schedulers.
- All data and graphs in this article are dummy.
1. What is Action Recognition?#
In this article, action recognition is defined as classifying an action from a video.
2. Required Environment and Brief Explanations#
I used the following tools to develop the model:
-
Google Colab Pro
- Used to run training and inference. In this article, a T4 GPU with High RAM is used.
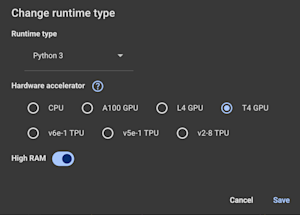
- Used to run training and inference. In this article, a T4 GPU with High RAM is used.
-
Weights & Biases (W&B)
- An AI developer platform consisting of three main products: Weave, Models, and Inference.
- In this article, Models is used to manage experiments.
- Also used to log evaluation metrics and optimise hyperparameters.
-
PyTorch
- Deep learning framework.
-
PyTorch Lightning
- A wrapper for PyTorch.
3. Environment Setup#
Before we start, we need to create a W&B account and place the dataset on Google Drive.
- Create a W&B account
- Annotate and place the video dataset on Google Drive
If the target classes are three, the directory structure is as follows:
Dataset
├── Train
│ ├── class1
│ │ ├── class1_01_t.mp4
│ │ ├── class1_02_t.mp4
│ │ ├── class1_03_t.mp4
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── class2
│ │ ├── class2_01_t.mp4
│ │ ├── class2_02_t.mp4
│ │ └── ...
│ └── class3
│ └── ...
└── Val
├── class1
│ ├── class1_01_v.mp4
│ ├── class1_02_v.mp4
│ ├── class1_03_v.mp4
│ └── ...
├── class2
│ └── ...
└── class3
└── ...
- Train/validation split
The appropriate ratio of training to validation data is usually between 6:4 and 8:2.
This task is basic action recognition, so we don’t need to specify the action area or the start and end times. Simply placing the files into the corresponding folders serves as the annotation.
4. Implementation for Training#
1. Mount drive and install libraries.
mount and define dataset path
from google.colab import drive drive.mount('/content/drive') WANDB_PROJECT = "3D ResNet" import os GOOFLE_DRIVE_DATASET_PATH = 'drive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/XXX/' TRAIN_VAL_DATASET_PATH = os.path.join(GOOFLE_DRIVE_DATASET_PATH, 'trial') print(os.listdir(TRAIN_VAL_DATASET_PATH)) # >> ['train', 'val']
Install libraries
%%capture !pip install fvcore !pip install av !pip install lightning !pip install wandb
Note: By adding %%capture in a cell, hide install logs.
2. Hyperparameter config
Login W&B
import wandb wandb.login()
Set hyperparameter config
By using W&B Sweeps, we can implement hyperparameter optimisation effectively.
sweep_config = { 'method': 'bayes' } metric = { 'name': 'val_loss', 'goal': 'minimize' } sweep_config['metric'] = metric parameters_dict = { 'num_epochs': { 'min': 10, 'max': 50 }, 'lr': { 'min': 5e-4, 'max': 1e-3, 'distribution': 'log_uniform_values', }, 'subsample':{ 'values': [13, 20, 30, 40] # controls temporal subsampling of video frames, x3d-s requires at least 13 frames. }, 'sampling_rate':{ 'values': [4] }, 'clip_duration':{ 'values': [2] }, 'batch_size':{ 'values': [24] }, 'num_workers':{ 'values': [8] }, 'data_path':{ 'values': [TRAIN_VAL_DATASET_PATH] }, } sweep_config['parameters'] = parameters_dict import pprint pprint.pprint(sweep_config) sweep_id = wandb.sweep(sweep_config, project=WANDB_PROJECT)
3. Data module function
By running torch.hub.list(), avoid inconsistency of torchvision and pytorchvideo without specifying version.
import torch Torch.hub.list('facebookresearch/pytorchvideo',force_reload=False
Define data modules.
import os import lightning as L import pytorchvideo.data import torch.utils.data from lightning.pytorch.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint from pytorchvideo.transforms import ( ApplyTransformToKey, Normalize, RandomShortSideScale, RemoveKey, ShortSideScale, UniformTemporalSubsample ) from torchvision.transforms import ( Compose, Lambda, RandomCrop, RandomHorizontalFlip, Resize, ColorJitter ) class KineticsDataModule(L.pytorch.LightningDataModule): # Dataset configuration def __init__(self, subsample, batch_size, num_workers, data_path, clip_duration): super().__init__() self.subsample = subsample self.batch_size = batch_size self.num_workers = num_workers self.data_path = data_path self.clip_duration = clip_duration def train_dataloader(self): train_transform = Compose( [ ApplyTransformToKey( key='video', transform=Compose( [ UniformTemporalSubsample(self.subsample), Lambda(lambda x: x / 255.0), Normalize((0.45, 0.45, 0.45), (0.225, 0.225, 0.225)), Resize((224, 224)), ] ) ) ] ) train_dataset = pytorchvideo.data.Kinetics( data_path=os.path.join(self.data_path, 'train'), clip_sampler=pytorchvideo.data.make_clip_sampler('random',self.clip_duration), decode_audio=False, transform=train_transform ) return torch.utils.data.DataLoader( train_dataset, batch_size=self.batch_size, num_workers=self.num_workers, pin_memory=True, persistent_workers=True ) def val_dataloader(self): val_transform = Compose( [ ApplyTransformToKey( key='video', transform=Compose( [ UniformTemporalSubsample(self.subsample), Lambda(lambda x: x / 255.0), Normalize((0.45, 0.45, 0.45), (0.225, 0.225, 0.225)), Resize((224, 224)), ] ) ) ] ) val_dataset = pytorchvideo.data.Kinetics( data_path=os.path.join(self.data_path, 'val'), clip_sampler=pytorchvideo.data.make_clip_sampler('uniform',self.clip_duration), decode_audio=False, transform=val_transform ) return torch.utils.data.DataLoader( val_dataset, batch_size=self.batch_size, num_workers=self.num_workers, pin_memory=True, persistent_workers=True )
4. Load a model and freeze layers.
Load a pretrained model and freeze all layers except classifier (Transfer learning).
Depending on the number of target classes, we need to change num_features (currently, num_features = 3).
def make_pretrained_resnet(freeze_backbone=True): model = torch.hub.load('facebookresearch/pytorchvideo', 'slow_r50', pretrained=True) # Freeze all layers if freeze_backbone: for param in model.parameters(): param.requires_grad = False # Replace classifier num_features = model.blocks[-1].proj.in_features model.blocks[-1].proj = torch.nn.Linear(num_features, 3) return model
5. Training function.
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F class VideoClassificationLightningModule(L.LightningModule): def __init__(self, learning_rate): super().__init__() self.model = make_pretrained_resnet() self.learning_rate = learning_rate self.save_hyperparameters() if wandb.run is not None: wandb.watch(self.model, log="all", log_freq=100) # Log model info trainable_params = sum(p.numel() for p in self.model.parameters() if p.requires_grad) total_params = sum(p.numel() for p in self.model.parameters()) wandb.log({ "model/trainable_parameters": trainable_params, "model/total_parameters": total_params, "model/frozen_ratio": (total_params - trainable_params) / total_params }) def forward(self, x): return self.model(x) def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx): y_hat = self.model(batch['video']) loss = F.cross_entropy(y_hat, batch['label']) self.log('train_loss', loss, prog_bar=True) self.log('learning_rate', self.optimizers().param_groups[0]['lr'], prog_bar=True) return loss def validation_step(self, batch, batch_idx): y_hat = self.model(batch['video']) loss = F.cross_entropy(y_hat, batch['label']) self.log('val_loss', loss) return loss def configure_optimizers(self): return torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=self.learning_rate) from lightning.pytorch.loggers import WandbLogger from lightning.pytorch import Trainer def train(): wandb.init(project=WANDB_PROJECT) config = wandb.config print("config",config) classification_module = VideoClassificationLightningModule( learning_rate=config.lr ) data_module = KineticsDataModule( subsample=config.subsample, batch_size=config.batch_size, num_workers=config.num_workers, data_path=config.data_path, clip_duration=config.clip_duration, ) wandb_logger = WandbLogger(log_model="all") trainer = Trainer( logger=wandb_logger, max_epochs=config.num_epochs, accelerator='auto', devices=1, ) trainer.fit(classification_module, data_module)
- Run Hyperparameter optimisation.
wandb.agent(sweep_id, train, count=10) #count is a number of trials wandb.finish()
We can check evaluation metrics on W&B dashboard.

5. Implementation for Inference#
1. Define inference function.
Depending on the target classes, we need to change class_names (currently, "Class A", "Class B", "Class C"). By defining the inference function as a another project, I managed inference results in another project (currently, project='inference_project').
import torch import os import wandb from pytorchvideo.data.encoded_video import EncodedVideo from torchvision.transforms import Compose, Lambda from torchvision.transforms._transforms_video import NormalizeVideo from pytorchvideo.transforms import ( ApplyTransformToKey, UniformTemporalSubsample, ShortSideScale, ) def run_inference(video_path, artifact_path): """ Run inference using trained model from W&B Args: video_path: Path to video file artifact_path: W&B artifact path """ wandb.init(project='inference_project') # Set device device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu" print(f"Using device: {device}") # Initialize W&B and download artifact print("Loading model from W&B...") artifact = wandb.use_artifact(artifact_path, type='model') artifact_dir = artifact.download() # Find and load the checkpoint (W&B downloads it for you) checkpoint_file = [f for f in os.listdir(artifact_dir) if f.endswith('.ckpt')][0] checkpoint_path = os.path.join(artifact_dir, checkpoint_file) # Load model directly from the downloaded checkpoint model = VideoClassificationLightningModule.load_from_checkpoint(checkpoint_path) model.eval() model = model.to(device) # Get the run that created this artifact run = artifact.logged_by() # Get config from the run config = run.config print(f"Model config: {config}") subsample = config['subsample'] sampling_rate = config['sampling_rate'] # Define class names class_names = [ "Class A", "Class B", "Class C" ] # Define input transform using config values transform = ApplyTransformToKey( key="video", transform=Compose([ UniformTemporalSubsample(subsample), Lambda(lambda x: x/255.0), NormalizeVideo([0.45, 0.45, 0.45], [0.225, 0.225, 0.225]), ShortSideScale(size=224), ]), ) clip_duration = 2 # Load and preprocess video print(f"Loading video: {video_path}") video = EncodedVideo.from_path(video_path) video_data = video.get_clip(start_sec=0, end_sec=clip_duration) # Apply transforms and prepare input video_data = transform(video_data) inputs = video_data["video"].to(device) # Run inference print("Running inference...") with torch.no_grad(): preds = model(inputs[None, ...]) # Get predictions post_act = torch.nn.Softmax(dim=1) preds = post_act(preds) pred_classes = preds.topk(k=3).indices[0] pred_scores = preds.topk(k=3).values[0] print("\nPredicted labels:") for i, (class_idx, score) in enumerate(zip(pred_classes, pred_scores)): print(f"{i+1}. {class_names[class_idx]}: {score:.4f}") wandb.finish() return pred_classes, pred_scores
2. Load a model from W&B and run inference.
Find the best model from the W&B Artifact, and load it.
video_path = os.path.join(GOOFLE_DRIVE_DATASET_PATH, 'sample.mp4') artifact_path = 'w&b_artifact_model_path' pred_classes, pred_scores = run_inference(video_path, artifact_path)
We can check the model path from W&B Artifact (Full Name is a model path).
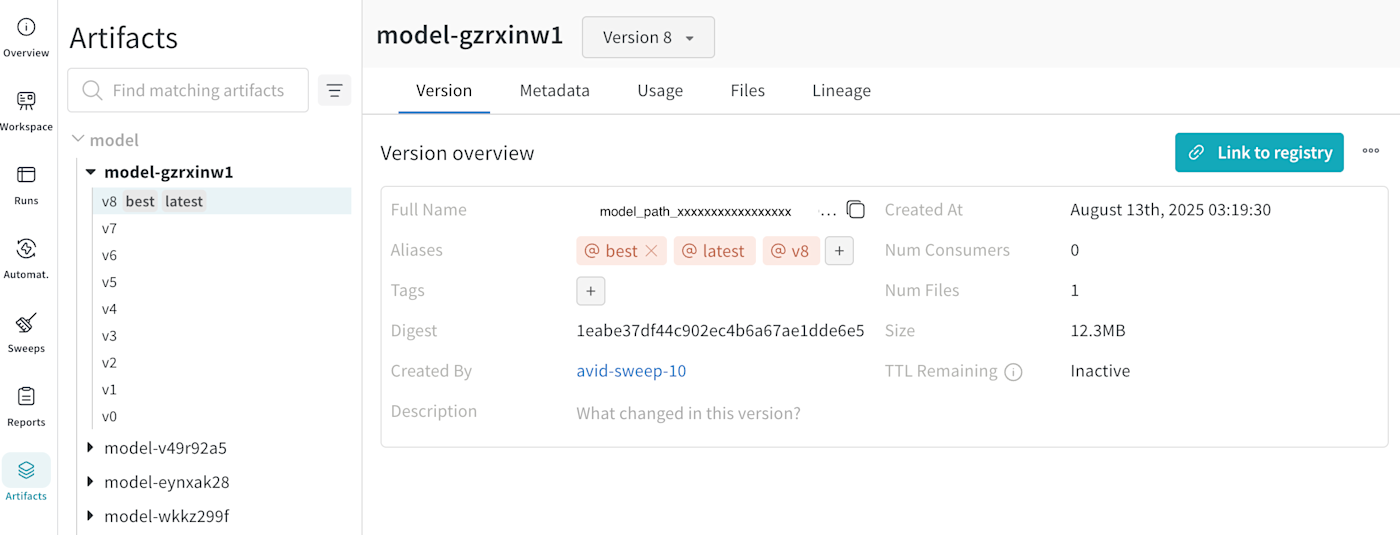
Output example:
Predicted labels:
1. Class A: 0.9042
2. Class B: 0.0838
3. Class C: 0.0119
